What Is The Muscle Spindle And How Does It Work?
The muscle spindle is a type of “sensor” located in skeletal muscles. One of its functions is to send information to the brain so that the person can recognize the state of their bones and muscles.
For example, the muscle spindle allows recognition of the state of contraction and stretching of muscle fibers. This is important to limit movement to avoid injury from overstretching or contraction. In other words, it helps the nervous system to continuously control the musculoskeletal system (muscles and bones).
Let’s see more below.
What are muscles and how do they work?
According to the scientific literature, muscles are the organs in charge of body movement. Are composed of cells called muscle fibers, capable of reacting to nerve stimuli. That is to say, when faced with an “order” from the brain, the muscles act.
Three types of muscles can be distinguished:
- Skeletal: these are the muscles that connect to the bones and allow the skeleton to move.
- Cardiac: it is found specifically in the wall of l heart and allows it to pump blood.
- Smooth or visceral: these are the muscles that are located in the walls of the hollow viscera, such as the intestines. These muscles move and aid in the digestion of food.
Muscle contraction
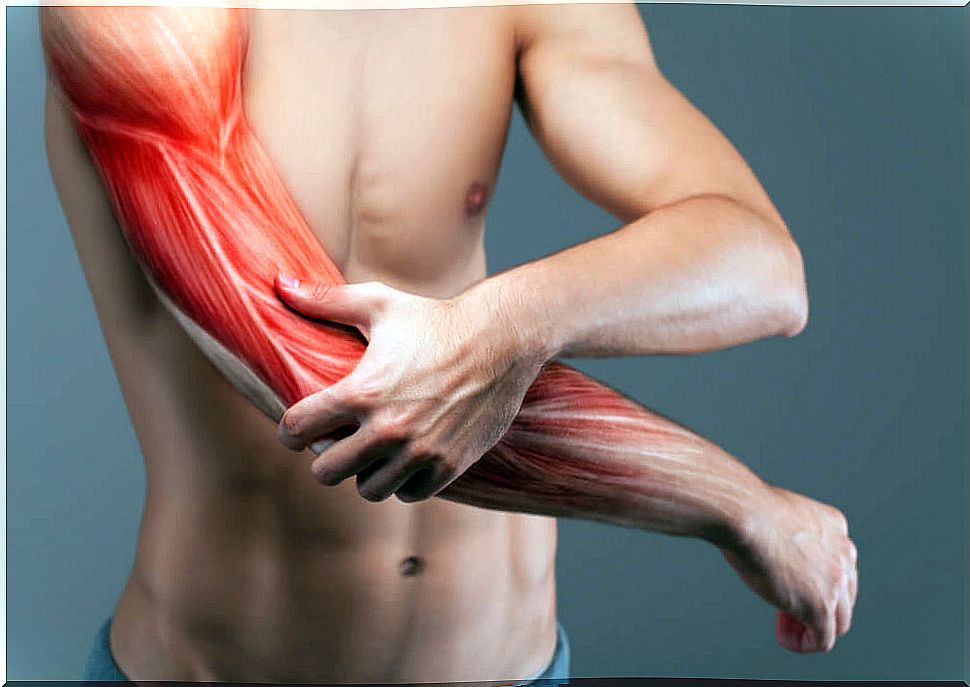
Muscle contraction occurs when signals from the nervous system reach the area where the neuron and the muscle join. Then the length of the muscle is reduced (this is voluntary in the case of skeletal muscles).
The role of the muscle spindle in contraction and stretching
As we have already said, the skeletal muscles have the function of contracting (shortening) and, successively, returning to their resting position (stretching). However, there must be a functional limit to this movement. This limit is monitored by the central nervous system through the muscle spindles.
This means that the muscle spindle informs the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) about the length of the muscle and the speed with which that length changes.
With this information, the nervous system controls muscle activity and protects the muscle from unforeseen tears and allows it to regulate movement and maintain posture.
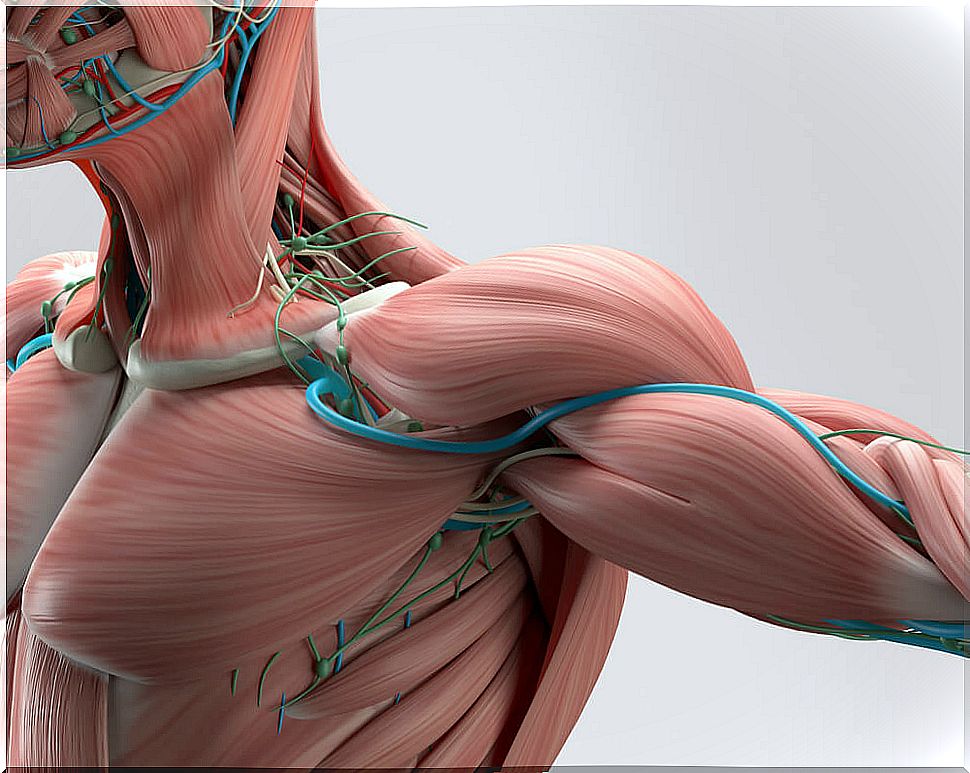
The muscle spindle has “nerve sensors” (sensory receptors) that are more sensitive to length than speed of stretch. That is, they can control the level of stretching of the muscle, depending on its length.
With this information, the muscle spindle generates an environment of functional relaxation before stretching. In this way, it prevents injuries due to muscle overstretching, or muscle strain.









