How Does The Mediterranean Diet Influence Intestinal Health?
In recent years, the effects of the Mediterranean diet on intestinal health have been investigated. Although it is a not so explored link, there are findings of certain benefits, especially in what has to do with the state of the microbiota.
This group of bacteria and microorganisms inhabits the digestive system and plays an important role in health. In fact, they are positively associated with a good functioning of the immune system, the proper metabolism of food, among others.
What does diet have to do with intestinal health? Why is the Mediterranean diet recommended? Following this topic, there are these and many other questions. Below we detail everything about it to get an answer.
Diet and intestinal flora
One of the organs most influenced by the quality of diet and lifestyle is, without a doubt, the intestine. In this organ live microorganisms that participate in different vital functions, such as digestion, the immune system, the inflammatory response or the synthesis of vitamins.
Thus, when the intestinal flora is healthy, balanced and ready to perform these functions, its characteristics are as follows:
- It has the right amount of beneficial microorganisms.
- There is no overgrowth of harmful microorganisms.
- Adequate microbial diversity is assured.
Regarding food and the microbiota, it should be noted that some foods enhance the activity of bacteria, already exert anti-inflammatory functions and favor the production of short-chain fatty acids.
In fact, fatty acids are one of the main sources of food for intestinal cells and can help keep the intestinal mucosa in good condition.

Mediterranean diet and intestinal health
The Mediterranean diet, in particular, is one of the most studied in terms of diet and health. Broadly speaking, we can say that the Mediterranean eating pattern is linked to a lower risk of suffering from chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease or diabetes, for example.
Now, a scientific study also associates this eating model with better gut health. Published in Gut magazine , it concludes that following a Mediterranean diet for a year can contribute to:
- Enhance the intestinal bacteria related to the brake of the frailty and cognitive decline.
- Reduce bacteria associated with an inflammatory state.
- Reduce the loss of bacteria diversity.
- Reduce the presence of pro-inflammatory substances that have harmful effects on health.
On this, it is important to mention that, although it is true that the results are positive and that they open the door to new research, the researchers admitted that the state of health of intestinal bacteria cannot be linked to diet alone. Thus, when talking about intestinal health, we must consider other factors that also influence its condition.
What are the characteristics of the Mediterranean diet for intestinal health?
Although the Mediterranean diet can vary somewhat depending on the region, in general it has a number of common characteristics. In its traditional form, it is based on the habitual intake of certain food groups. Specifically, it has the following characteristics:
- Extra virgin olive oil is the main source of fat, both for cooking and for dressing.
- Vegetables are consumed daily and green leafy ones stand out.
- Contains fruits and whole grains.
- Nuts and legumes are included in moderation.
- Includes fish (especially blue), meat and dairy products in moderation.
- It contains low amounts of red meat and saturated fat.
According to the evidence, there are some of these foods that are more beneficial in terms of intestinal health. What are they and why are they important? Let’s see in detail below.
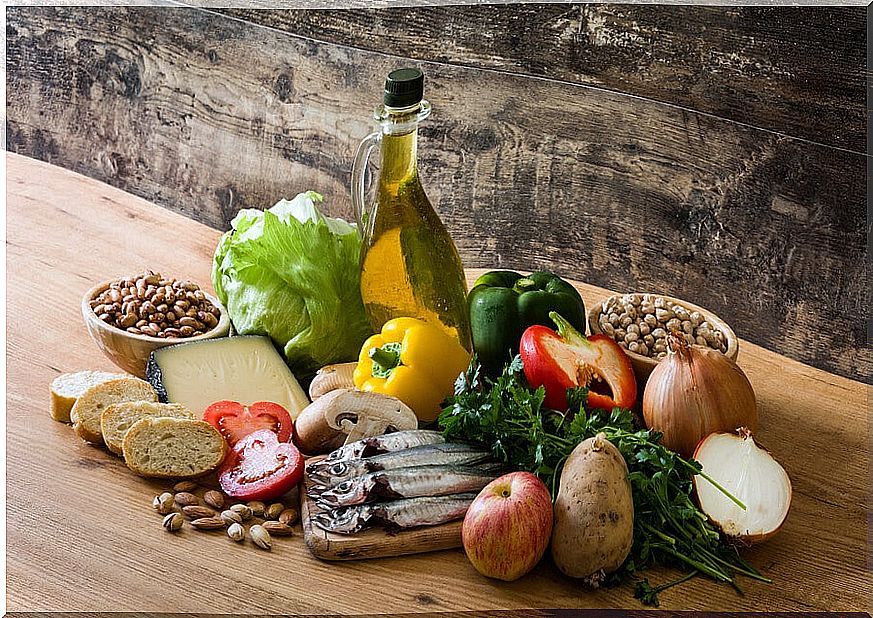

1. Fatty acids
In this case, an optimal intake of mono and polyunsaturated fatty acids stands out, accompanied by a low consumption of saturated fats. This lipid profile is beneficial, as it is associated with very low inflammatory markers.
2. Carbohydrates accessible to the microbiota
The intake of this type of fiber is also present, which is also known by the name of Mac’s. This carbohydrate cannot be digested, since the body does not have the necessary enzymes to do so. In this way, it reaches the colon intact where it is fermented by bacteria.
From there, a series of positive compounds are derived for the health of the colon, apart from serving as food for microorganisms. In general, studies have found higher levels of short-chain fatty acids in the feces of people who regularly ate a Mediterranean diet.
3. Polyphenols
Polyphenols are present in this type of diet, since it is abundant in fruits, vegetables, olive oil and aromatic herbs. These compounds have been included within the group of prebiotic foods, that is, those that nourish intestinal bacteria. Phenols act positively for two reasons:
- They increase the diversity of gut microbes.
- They help prevent the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
Other healthy habits for the gut microbiota
Diet is one of the most determining factors in the composition of the intestinal flora, but not the only one. Certain environmental and lifestyle aspects also influence your condition. It is known, for example, that stress negatively affects the gut; likewise, insufficient rest and lack of physical exercise.
In addition, when we talk about food, not only what we eat influences, but also how we do it. Therefore, it is convenient to eat slowly and ensure optimal hydration. Finally, to avoid alterations in these bacteria, it is best to abandon harmful habits such as the consumption of alcohol and tobacco.

The Mediterranean diet is also good for intestinal health
The well-done Mediterranean diet, with traditional, fresh and little-elaborated foods is one of the healthiest in terms of health. Apart from its known benefits at the vascular and cerebral level, now we can also add benefits at the intestinal level, since it contains foods and nutrients that are ideal for the microbiota.